What are Treehoppers?
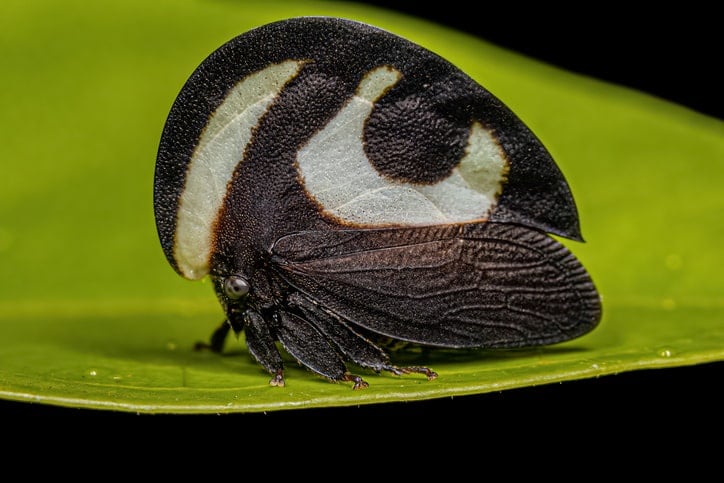
Treehoppers are fascinating insects that belong to the family Membracidae. They are known for their unique physical appearance, which varies greatly from species to species. Generally, Treehoppers have a rounded body shape and a distinctive, enlarged pronotum that protrudes from the back of their head. This pronotum can take on a variety of shapes, from spiky and horned to flat and leaf-like, depending on the species.
What do Treehoppers Look Like?
Many Treehoppers also have brightly colored and patterned bodies, which make them easy to spot amidst leaves and branches. With over 3,000 known species of Treehoppers, each with its own distinct look, there is a lot of variety to appreciate in this fascinating family of insects.
Behavior of Treehoppers
Some scientists think that Treehoppers model themselves after the Ophiocordyceps fungus, a type of fungus which takes control of its host, kills it, and then sprouts a flower through their head. The flower then erupts and spreads more fungal seeds all over the ground onto more bugs. Scientists believe that some insects which know what the disease is may avoid attempting to prey on the Treehopper because it doesn’t want to receive the disease.
Other Treehoppers may camouflage themselves as having poisonous colors in order to appear distasteful, which may save themselves from being eaten. Some species of Treehoppers even mimic ants that have mandibles or stingers, so if a predator sees them it may get scared. However, Treehoppers don’t actually have any mandibles or stingers and are actually pretty defenseless.
Life Cycle of Treehoppers
Treehoppers have a unique life cycle, which starts when the female lays her eggs on the underside of tree branches or leaves. After hatching, the nymphs go through several molts, shedding their skin as they grow. During this stage, they feed on plant sap using their piercing-sucking mouthparts.
Once the nymphs reach maturity, they develop wings and become adults. Adult Treehoppers can be identified by their modified pronotum, which often resembles thorns or spines and makes them difficult to spot. They use their wings to fly from tree to tree, feeding on plant sap and reproducing. The life cycle of Treehoppers is typically completed within a year, with multiple generations occurring annually in warmer climates. Despite their small size, Treehoppers play an essential role in the ecosystem as food for predators and pollinators of certain plants.
How to Control Treehoppers
Controlling treehoppers can be challenging because they are mobile and can move from one plant to another quickly. However, there are several strategies that gardeners can use to manage infestations. One effective method is to physically remove the insects by handpicking them or using a strong jet of water to dislodge them from plants.
However, attempting to control these pests without professional help isn’t always effective in the long term. At Hulett Environmental Services, we provide sustainable pest control solutions that give you peace of mind knowing your home or business will be pest-free.
Schedule Your Free Inspection with Hulett Today
Don’t wait to control pests that are invading your space. While most pests, such as Treehoppers may seem like a nuisance, they can impose risks as they can chew on electrical equipment and bite if threatened. Our team of pest control professionals have over 50 years of experience in the pest control industry and are committed to helping you return to living pest-free. Schedule your free inspection today by giving our team a call or filling out our online form!