Active Seasons




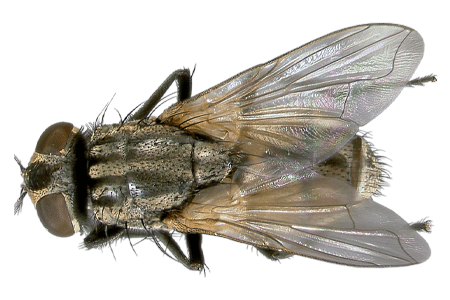
Fly Appearance and Size Facts
One of the most common pests, flies can be a real nuisance. Their constant buzzing can put a damper on family meals and make you dread being in your kitchen. If you’re dealing with a fly infestation at your business, they can leave a bad first impression on customers.
A few of their common characteristics include:
- One pair of primary wings and large, distinct eyes
- Varying in color, typically ash brown or gray, but sometimes green or yellow
- 0.01 inches (0.25 millimeters) to 1.5 inches in length
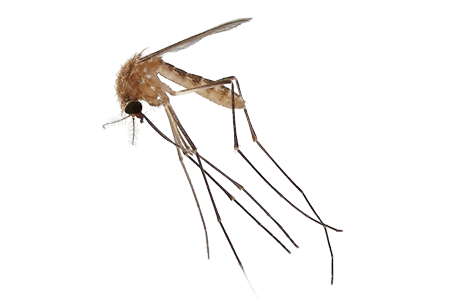
There are more than 100,000 species of flies around the world, with more than 15,000 of them native to North America. Two of the most common types of flies include house flies and mosquitoes.
We offer fly control in the following locations and their surrounding areas:
Types of Flies

Behavior and Habitat of Flies
You may know flies for their annoying buzzing and intrusive flying around your home. They can be especially active when you are eating or cooking, as they try to get to your food.
Flies thrive most in filth, such as garbage, feces, and decay, which is why they can pose threats to humans who come in contact with them. Research shows that flies can carry up to 65 different diseases, which they can transmit to humans, including food poisoning, typhoid, dysentery, cholera, tuberculosis, and more.

Signs of Infestation of Flies
Since flies are highly invasive, if you’re dealing with a fly infestation, you’ll likely see and hear these annoying insects. Often, if one fly is in your space, another will follow right behind it. While a solitary fly may not be a cause for concern, a large number of them can get annoying quickly.

Tips for Prevention of Flies
Flies can be attracted by exposed trash, decaying matter, overripe fruit, spoiled food, and pet waste. Some species of flies are attracted to leaky pipes, standing water, or bright light as well.
Since so many different things can attract flies, one of the best ways to prevent flies is to ensure all entry points are sealed up, including window screens, door cracks, or gaps in siding. Dispose of rotten foods and overripe fruit right away and clean regularly to avoid attracting flies.
Getting Rid of Flies
Once you’re dealing with a swarm of flies, getting rid of them can be difficult. Store-bought traps can sometimes work on a few straggling flies but can often damage your home or detract from its beauty without the effectiveness needed to wipe out a full infestation. Swatting flies can be a temporary fix but not a long-term solution. Instead, count on the professionals at Hulett.
Effective Fly Control Solutions
If you’ve tried everything you can think of and you’re still dealing with those pesky flies, it’s time for effective fly control from Hulett. We have over 50 years of experience providing pest control in south Florida, so our expert technicians can help you get rid of the swarm of flies in your home or a whole host of other pest problems.
Take the first step toward a healthy, pest-free home today. Sign up for a free inspection or give us a call to get started!